

The letters of the alphabet that usually represent the consonant sounds are: b, c, d, f, g, h, j, k, l, m, n, p, q, r, s, t, v, w, x, y, z.
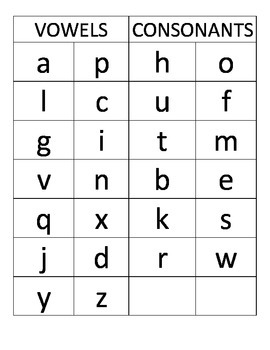
This means that the jaw doesn’t drop noticeably, which is different to vowel sounds. The letter ‘y’ is sometimes referred to as an honorary vowel as it is used to replace one of the other vowel letters in words such as: fly or my.Īll words in the English language have at least one vowel sound in them so the written version must have at least one vowel letter in it.Ĭonsonant sounds are made (produced) when the air flow is being restricted in some way, for example, changes in tongue position resulting in the mouth not opening as wide. The letters of the alphabet that we normally associate as being the vowel letters are: a, e, i, o and u. These can often be held without distorting their sound.
‘Long’ vowel sounds, due to the length of their pronunciation. The sound cannot be held onto without becoming distorted Vowels and consonants are sounds not letters, Vowels are the loud sounds that form the nuclei of each syllable, and consonants separate them. ‘Short’ vowel sounds, due to the short duration of the sound being made. Vowel sounds are usually (in the UK Education System) split into two main categories based on sound quality: Vowel sounds allow the air to flow freely, causing the chin to drop noticeably, whilst consonant sounds are produced by restricting the air flow. In our written language we refer to the letters of the alphabet as being consonant or vowel letters depending on which type of sound they are representing. The English Language is created through the different combinations of 44 sounds (phonemes), 20 vowels and 24 consonants.






 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
